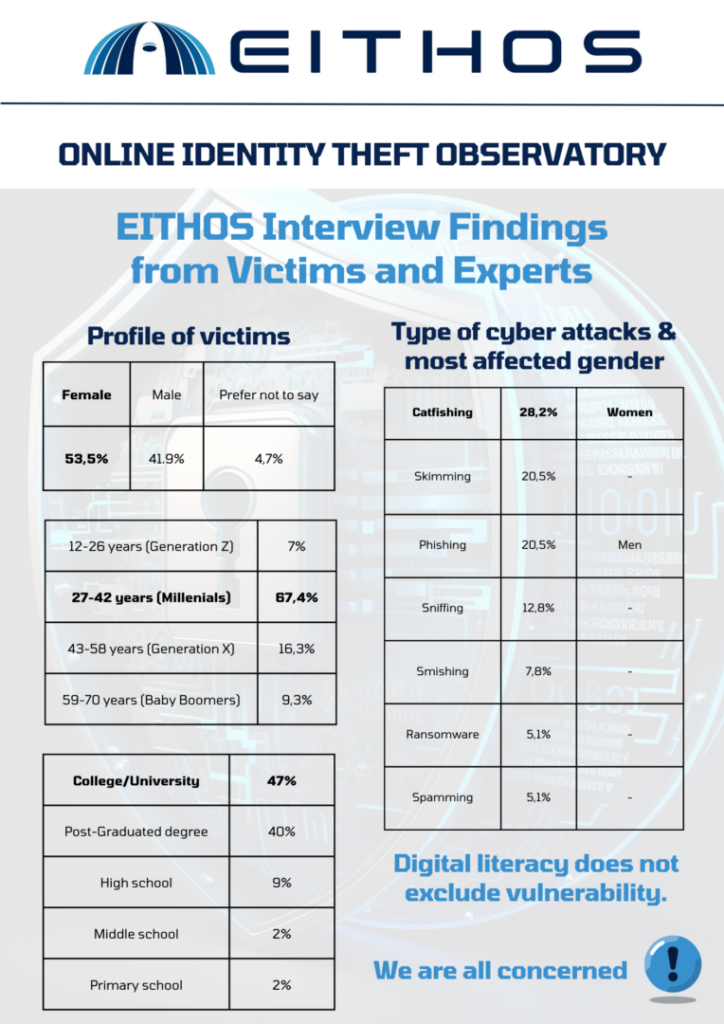
An internal report from Bologna University profiles the typical victims of OIDT (Online Identity Theft). Contrary to expectations, those most affected by identity theft tend to be more educated individuals. Furthermore, a gender analysis by the researcher reveals two distinct patterns: women are more frequently targeted by catfishing scams, while men are more susceptible to phishing attacks.
How to Avoid Creating More Victims
With this data, it is possible to implement tailored prevention strategies to avoid adverse situations such as financial losses, data breaches, and damage to reputations.
Based on these insights, the following actions are necessary:
- Enhance identity theft prevention campaigns targeting high school and university students, as well as the workplace.
- Develop specific campaigns against catfishing and phishing, focusing on women and men, respectively.
- Create educational campaigns that clearly explain various digital threats and their mechanisms, as understanding these is the first step in preventing them.
These measures are crucial for mitigating future attacks.
